Get Postgres Tips and Tricks
Subscribe to get advanced Postgres how-tos.
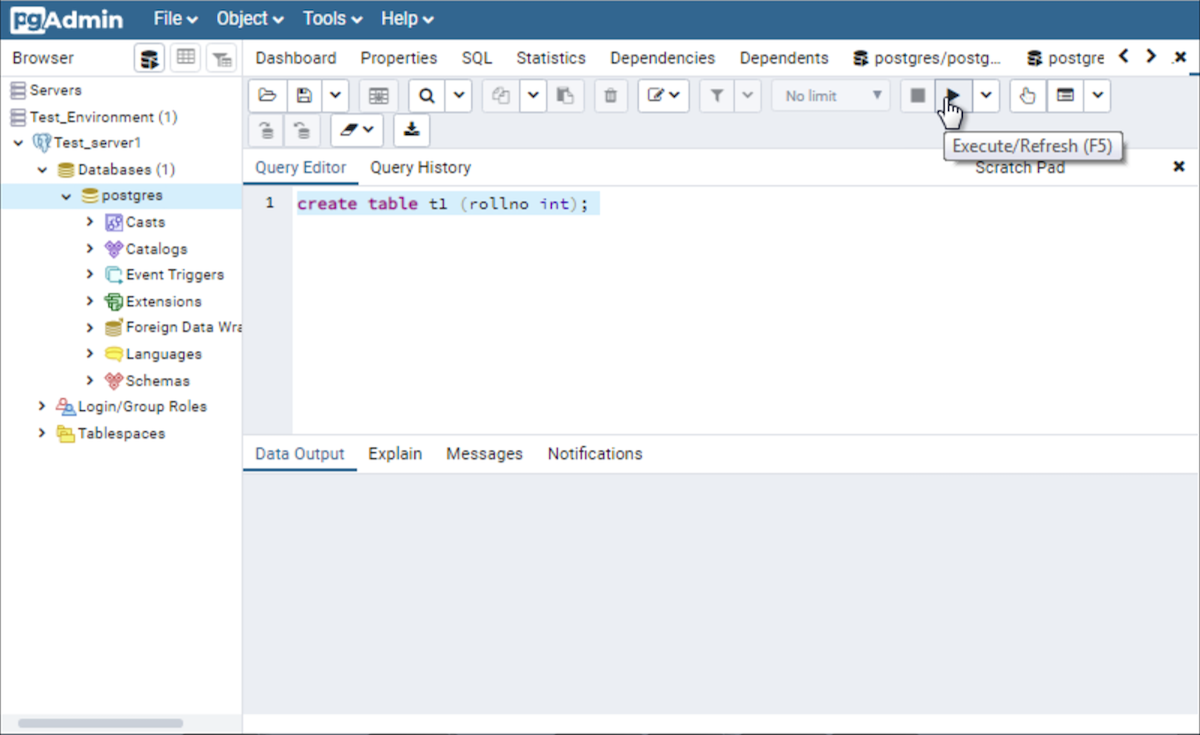
Installing PostgreSQL in Ubuntu 20.04. Log into your Ubuntu system and update the system. The correct Answer by richyen explains how the host-based access settings of pghba.conf file are not editable by pgAdmin 4. So we must use a text-editor to edit the pghba.conf file directly. Example on macOS. Here is an example of using an editor to do so, the command-line tool nano, on macOS (and possibly on BSD). Forgotten your password?
Welcome to pgAdmin 4. pgAdmin is the leading Open Source management tool forPostgres, the world’s most advanced Open Source database. pgAdmin 4 is designedto meet the needs of both novice and experienced Postgres users alike, providinga powerful graphical interface that simplifies the creation, maintenance and useof database objects.
- Getting Started
- Connecting To A Server
- Managing Cluster Objects
- Managing Database Objects
- Creating or Modifying a Table
- Management Basics
- Backup and Restore
- Developer Tools
- pgAgent
- pgAdmin Project Contributions
- Release Notes
NOTE: We are in the process of modifying the file structure and configuration for many Bitnami stacks. On account of these changes, the file paths stated in this guide may change depending on whether your Bitnami stack uses native Linux system packages (Approach A), or if it is a self-contained installation (Approach B). To identify your Bitnami installation type and what approach to follow, run the command below:
The output of the command indicates which approach (A or B) is used by the installation, and will allow you to identify the paths, configuration and commands to use in this guide. Refer to the FAQ for more information on these changes.

NOTE: This section assumes that you have downloaded and installed pgAdmin 4.
pgAdmin is the most popular and feature-rich platform for administration and development of PostgreSQL databases. Check the pgAdmin official page for more information.
To connect to your remote PostgreSQL database server using pgAdmin 4, follow these steps:
NOTE: In the steps below, you will be modifying a couple of PostgreSQL configuration files. Depending on your installation type, these files will be located in the following paths:
Pgadmin 4 Download Windows
Approach A (Bitnami installations using system packages):
- PostgreSQL configuration settings file: /opt/bitnami/postgresql/conf/postgresql.conf
- PostgreSQL client authentication configuration file: /opt/bitnami/postgresql/conf/pg_hba.conf
Approach B (Self-contained Bitnami installations):
- PostgreSQL configuration settings file: /opt/bitnami/postgresql/data/postgresql.conf
- PostgreSQL client authentication configuration file: /opt/bitnami/postgresql/data/pg_hba.conf
Make sure that you have your cloud server’s IP address and application credentials (instructions).
Open port 5432 in the server firewall (instructions).
IMPORTANT: By default, the database port for the nodes in this solution cannot be accessed over a public IP address. As a result, you will only be able to connect to your database nodes from machines that are running in the same network. For security reasons, we do not recommend making the database port accessible over a public IP address. If you must make it accessible over a public IP address, we recommend restricting access to a trusted list of source IP addresses using firewall rules. For development purposes, you can also use a VPN or SSH tunnel. Refer to the FAQ for information on accessing restricted ports using an SSH tunnel or opening ports in the server firewall.
Connect to your cloud server using PuTTY or another SSH client (instructions).
At the server console, edit the PostgreSQL client authentication configuration file pg_hba.conf and add the following at the end, then save the file:
Edit the PostgreSQL configuration file postgresql.conf file and replace this line
with:
Save the file.
Restart the PostgreSQL server:
Pgadmin 4 Tutorial
Your PostgreSQL server is now configured to accept remote connections, and you can connect to it using pgAdmin 4. Follow these steps:
Launch pgAdmin 4.
Go to the “Dashboard” tab. In the “Quick Link” section, click “Add New Server” to add a new connection.
Select the “Connection” tab in the “Create-Server” window.
Then, configure the connection as follows:
Enter your server’s IP address in the “Hostname/Address” field.
Specify the “Port” as “5432”.
Enter the name of the database in the “Database Maintenance” field.
Enter your username as postgres and password (use the same password you used when previously configuring the server to accept remote connections) for the database.
Click “Save” to apply the configuration.
Check that the connection between pgAdmin 4 and the PostgreSQL database server is active. Navigate to the “Dashboard” tab and find the state of the server in the “Server activity” section: