Element Argon - Ar
Name: Argon: Symbol: Ar: Atomic Number: 18: Atomic Mass: 39.948 atomic mass units: Number of Protons: 18: Number of Neutrons: 22: Number of Electrons: 18: Melting.
Comprehensive data on the chemical element Argon is provided on this page; including scores of properties, element names in many languages, most known nuclides of Argon. Common chemical compounds are also provided for many elements. In addition technical terms are linked to their definitions and the menu contains links to related articles that are a great aid in one's studies.
Argon Menu
- Argon Page One
- Argon Page Two
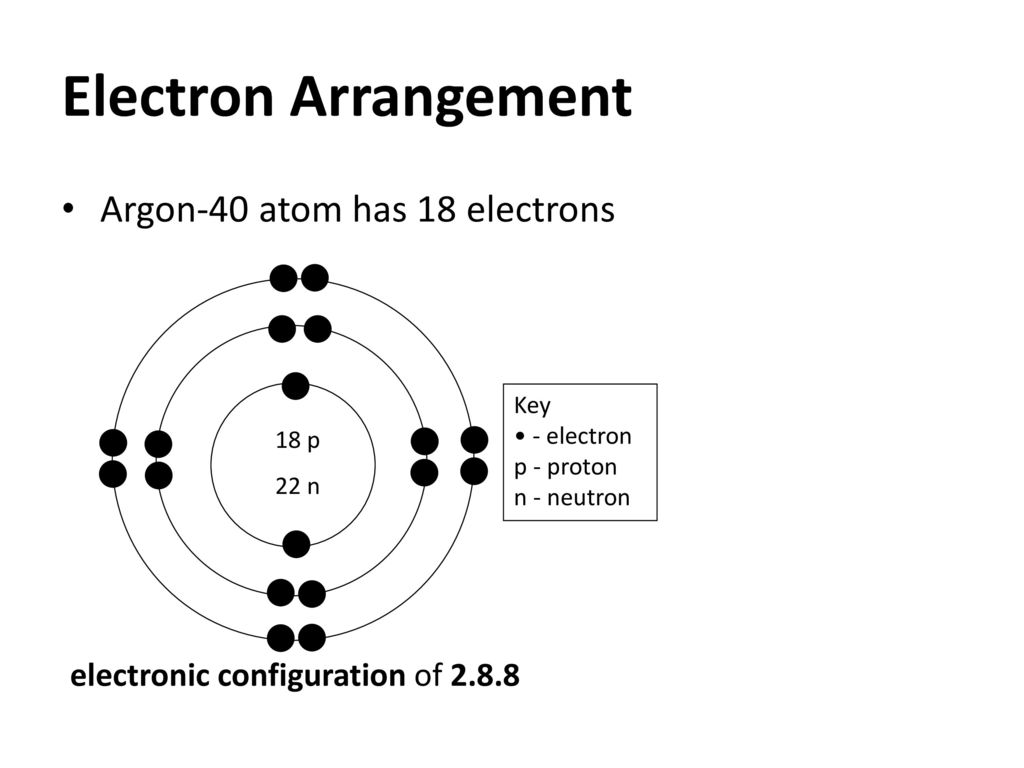
- Argon Ar Element 18 Mass Number: 40 Atomic weight: 39.963 g/mol Atomic number (Z): 18 Electrons: 18 Protons: 18 Neutrons: 22 Period: 3 Group: 18 Block: p.
- The complete octet (eight electrons) in the outer atomic shell makes argon stable and resistant to bonding with other elements. Its triple point temperature of 83.8058 K is a defining fixed point in the International Temperature Scale of 1990. Argon is extracted industrially by the fractional distillation of liquid air.
- Double glazing is even more efficient if the gap between the two panes of glass is filled with argon rather than just air because argon is a poorer conductor of heat. Thermal conductivity of argon at room temperature (300 K) is 17.72 mW m -1 K -1 (milliWatts per metre per degree) whereas for air it is 26 mW m -1 K -1.
Overview of Argon
- Atomic Number: 18
- Group: 18
- Period: 3
- Series: Noble Gasses
Argon's Name in Other Languages
- Latin: Argon
- Czech: Argon
- Croatian: Argon
- French: Argon
- German: Argon - r
- Italian: Argo
- Norwegian: Argon
- Portuguese: Argônio
- Russian: Аргон
- Spanish: Argón
- Swedish: Argon
Atomic Structure of Argon

- Atomic Radius: 0.88Å
- Atomic Volume: 28.5cm3/mol
- Covalent Radius: 0.98Å
- Cross Section (Thermal Neutron Capture)σa/barns: 0.675
- Crystal Structure: Cubic face centered
- Electron Configuration:
- 1s2 2s2p6 3s2p6
- Electrons per Energy Level: 2,8,8
- Shell Model
- Shell Model
- Ionic Radius:
- Filling Orbital: 3p6
- Number of Electrons (with no charge): 18
- Number of Neutrons (most common/stable nuclide): 22
- Number of Protons: 18
- Oxidation States: 0
- Valence Electrons: 3s2p6
- Electron Dot Model
- Electron Dot Model
Chemical Properties of Argon
- Electrochemical Equivalent:
- Electron Work Function:
- Electronegativity: N/A (Pauling); 3.2 (Allrod Rochow)
- Heat of Fusion: 1.188kJ/mol
- Incompatibilities:
- Ionization Potential
- First: 15.759
- Second: 27.629
- Third: 40.74
- Valence Electron Potential (-eV):
Physical Properties of Argon
- Atomic Mass Average: 39.948
- Boiling Point: 87.45K -185.7°C -302.3°F
- Coefficient of lineal thermal expansion/K-1: N/A
- Conductivity
- Electrical:
Thermal: 0.0001772 W/cmK
- Electrical:
- Density: 1.7824g/L @ 273K & 1atm
- Description:
- Colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas.
- Enthalpy of Fusion: 1.18 kJ/mole
- Enthalpy of Vaporization: 6.43 kJ/mole
- Flammablity Class:
- Freezing Point:see melting point
- Heat of Vaporization: 6.447kJ/mol
- Melting Point: 83.96K -189.19°C -308.54°F
- Molar Volume: 24.2 cm3/mole
- Optical Refractive Index: 1.000281
- Physical State (at 20°C & 1atm): Gas
- Specific Heat: 0.52J/gK
Regulatory / Health
- CAS Number
- 7440-37-1
- UN/NA ID and ERG Guide Number
- UN1006
- RTECS: CF2300000
- OSHAPermissible Exposure Limit (PEL)
- No limits set by OSHA
- OSHA PEL Vacated 1989
- No limits set by OSHA
- NIOSHRecommended Exposure Limit (REL)
- No limits set by NIOSH
- Levels In Humans:
Note: this data represents naturally occuring levels of elements in the typical human, it DOES NOT represent recommended daily allowances.- Blood/mg dm-3: trace
- Bone/p.p.m: nil
- Liver/p.p.m: nil
- Muscle/p.p.m: nil
- Daily Dietary Intake: n/a
- Total Mass In Avg. 70kg human: n/a
Argon Number Of Protons
Who / Where / When / How
- Discoverer: Sir William Ramsey, Lord Baron Rayleigh
- Discovery Location: Bristol England (Ramsey)/London England (Rayleigh)
- Discovery Year: 1894
- Name Origin:
- Greek: Argos (inactive).
- Abundance of Argon:
- Earth's Crust/p.p.m.: 1.2
- Seawater/p.p.m.: 0.45
- Atmosphere/p.p.m.: 9300
- Sun (Relative to H=1E12): 1000000
- Sources of Argon:
- Argon makes up 1% of the air and is isolated by removing nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and water from air. Argon is constantly being formed from the radioactive decay of K-40 (an isotope of potassium). of radioactive potassium-40. World wide commercial production is around 700,000 tons per year.
- Uses of Argon:
- Argon is used for lighting. It may also be used to provide an inert atmosphere for certain projects when explosion or other forms of oxidation may pose a problem. Also used in 'Geiger' counters, which measure radiation levels.
- Additional Notes:
Argon Menu
- Argon Page One
- Argon Page Two
References
A list of reference sources used to compile the data provided on our periodic table of elements can be found on the main periodic table page.
Related Resources
- Anatomy of the Atom
Answers many questions regarding the structure of atoms. - Molarity, Molality and Normality
Introduces stoichiometry and explains the differences between molarity, molality and normality. - Molar Mass Calculations and Javascript Calculator
Molar mass calculations are explained and there is a JavaScript calculator to aid calculations. - Chemical Database
This database focuses on the most common chemical compounds used in the home and industry.
Citing this page
If you need to cite this page, you can copy this text:
Kenneth Barbalace. Periodic Table of Elements - Argon - Ar. EnvironmentalChemistry.com. 1995 - 2021. Accessed on-line: 4/25/2021
https://EnvironmentalChemistry.com/yogi/periodic/Ar.html
.
Linking to this page
If you would like to link to this page from your website, blog, etc., copy and paste this link code (in red) and modify it to suit your needs:
<a href='https://EnvironmentalChemistry.com/yogi/periodic/Ar.html'>echo Periodic Table of Elements: Argon - Ar (EnvironmentalChemistry.com)</a>- Comprehensive information for the element Argon - Ar is provided by this page including scores of properties, element names in many languages, most known nuclides and technical terms are linked to their definitions.
.
NOTICE: While linking to articles is encouraged, OUR ARTICLES MAY NOT BE COPIED TO OR REPUBLISHED ON ANOTHER WEBSITE UNDER ANY CIRCUMSTANCES.
Argon Number Of Electrons Gained Or Lost
PLEASE, if you like an article we published simply link to it on our website do not republish it.
